
Cisco CUCM generates multiple record types, but CDR (Call Detail Records) and CMR (Call Management Records) serve very different purposes once you get past the acronyms.
Engineer's Quick Take: If you’re troubleshooting routing, validating call flow, or chasing down a quality complaint, knowing which dataset answers which question matters. CDR shows what happened; CMR helps explain why the experience was good or bad.
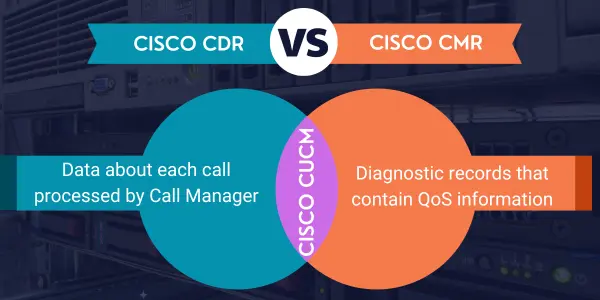
CDRs are generated by Cisco Call Manager (CUCM) to record call signaling activity. They tell you what the call did inside the call control layer.
CDR answers questions like:
Did the call route where I expected it to?
Which device, gateway, or trunk handled the call?
How long was the call actually connected?
Note: Detailed CDR field definitions and termination causes are documented in our technical reference.
CMRs are generated when CUCM establishes media streams. Instead of signaling, they focus on what happened to the RTP media once the call was up.
📊 Voice and video quality troubleshooting
📊 Network performance validation
📊 Analyzing jitter, latency, packet loss, and MOS
Why did users report poor audio?
Was the issue network-related or endpoint-related?
Did quality degrade mid-call?
Note: Not every call produces a CMR. Short calls, failed calls, or signaling-only events may still generate a CDR with no corresponding CMR.
| Area | CDR | CMR |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Call control & signaling | Media quality & performance |
| Generated when | Call is processed by CUCM | Media streams are established |
| Typical data | Start/end time, duration, route | Jitter, latency, packet loss, MOS |
| Primary use | Routing, usage, accounting | QoE and network troubleshooting |
Most real-world troubleshooting requires correlating both datasets. For example:
Correlation—not replacement—is the key. Analyzing raw logs is complex, which is why tools like XT2 Telemanagement or Expo XT are used to bridge these data points automatically.
You can confirm the call happened and how long it lasted, but CDRs don’t contain media metrics. For quality issues, you’ll need CMR data to see jitter and packet loss.
This happens because the call never established media (e.g., a busy signal), ended too quickly, or failed during signaling. This is expected behavior in CUCM.
Not always. They are generated by different processes, which is why robust correlation logic is required when using third-party reporting tools.
The concepts carry over, but record structures differ. Cloud-specific datasets are covered in our Webex Calling analytics articles.
